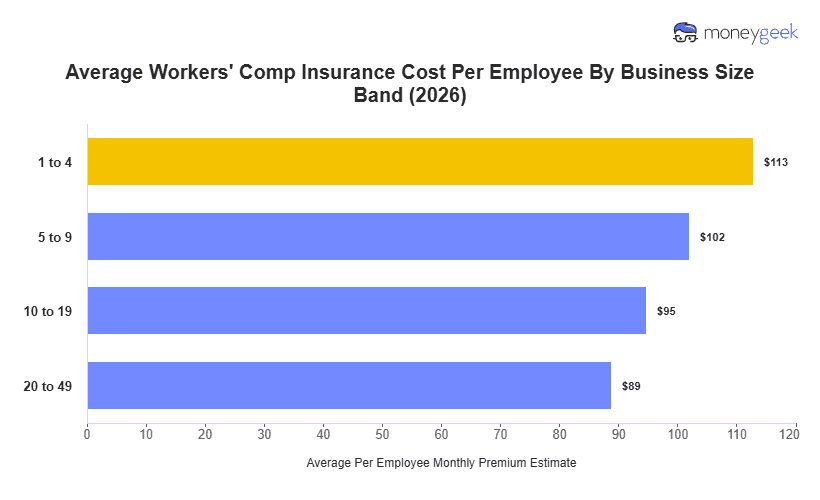
Workers' comp insurance costs an average of $113 per employee monthly ($1,354 per employee annually) for businesses with one to four employees across 408 industries and 46 states plus Washington, D.C.
This is a benchmark, not a quote. Insurers adjust workers' comp rates based on industry risk (how often and how severely injuries occur), business size (total payroll) and location (state-specific regulations).